What Is Mortons Neuroma
Overview
 Morton?s neuroma is inflammation, thickening, or enlargement of the nerve between the bones of the toes (metatarsal bones). The condition is also called intermetatarsal neuroma. The thickening is usually found between bones of the third and fourth toes of the foot, but sometimes it may develop between the second and third toes. It occurs when the medial plantar nerve near the bones of those toes becomes compressed or irritated, possibly because the metatarsal bones press against the nerve in the narrow gap between the toes. If left untreated, Morton?s neuroma can cause a sharp, burning, or shooting pain that often gets worse over time. The pain becomes worse when a person walks or stands on the ball of the foot. Sometimes the pain reaches the toes next to the neuroma and a sensation of tingling or numbness is felt.
Morton?s neuroma is inflammation, thickening, or enlargement of the nerve between the bones of the toes (metatarsal bones). The condition is also called intermetatarsal neuroma. The thickening is usually found between bones of the third and fourth toes of the foot, but sometimes it may develop between the second and third toes. It occurs when the medial plantar nerve near the bones of those toes becomes compressed or irritated, possibly because the metatarsal bones press against the nerve in the narrow gap between the toes. If left untreated, Morton?s neuroma can cause a sharp, burning, or shooting pain that often gets worse over time. The pain becomes worse when a person walks or stands on the ball of the foot. Sometimes the pain reaches the toes next to the neuroma and a sensation of tingling or numbness is felt.
Causes
A Morton's neuroma commonly occurs due to repetitive weight bearing activity (such as walking or running) particularly when combined with tight fitting shoes or excessive pronation of the feet (i.e. "flat-feet"). The condition is also more common in patients with an unstable forefoot allowing excessive movement between the metatarsal bones. A Morton's neuroma can also occur due to certain foot deformities, trauma to the foot, or the presence of a ganglion or inflamed bursa in the region which may place compressive forces on the nerve.
Symptoms
Symptoms associated with a neuroma include a dull burning sensation radiating towards the toes, a cramping feeling, or even a stinging, tingling sensation that can be described as being similar to an electric shock. It is often worse when wearing shoes with most people finding the pain disappears when removing their shoes.
Diagnosis
To diagnose Morton's neuroma the podiatrist commonly palpates the area to elicit pain, squeezing the toes from the side. Next he or she may try to feel the neuroma by pressing a thumb into the third interspace. The podiatrist then tries to elicit Mulder's sign, by palpating the affected interspace with one hand and squeezing the entire foot at the same time with the other hand. In many cases of Morton's neuroma, this causes an audible click, known as Mulder's sign. An x-ray should be taken to ensure that there is not a fracture. X-rays also can be used to examine the joints and bone density, ruling out arthritis (particularly rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis).
Non Surgical Treatment
Sclerosing alcohol injections are an increasingly available treatment alternative if the above management approaches fail. Dilute alcohol (4%) is injected directly into the area of the neuroma, causing toxicity to the fibrous nerve tissue. Frequently, treatment must be performed 2-4 times, with 1-3 weeks between interventions. An 60-80% success rate has been achieved in clinical studies, equal to or exceeding the success rate for surgical neurectomy with fewer risks and less significant recovery. If done with more concentrated alcohol under ultrasound guidance, the success rate is considerably higher and fewer repeat procedures are needed. Radio Frequency Ablation is also used in the treatment of Morton's Neuroma The outcomes appear to be equally or more reliable than alcohol injections especially if the procedure is done under ultrasound guidance.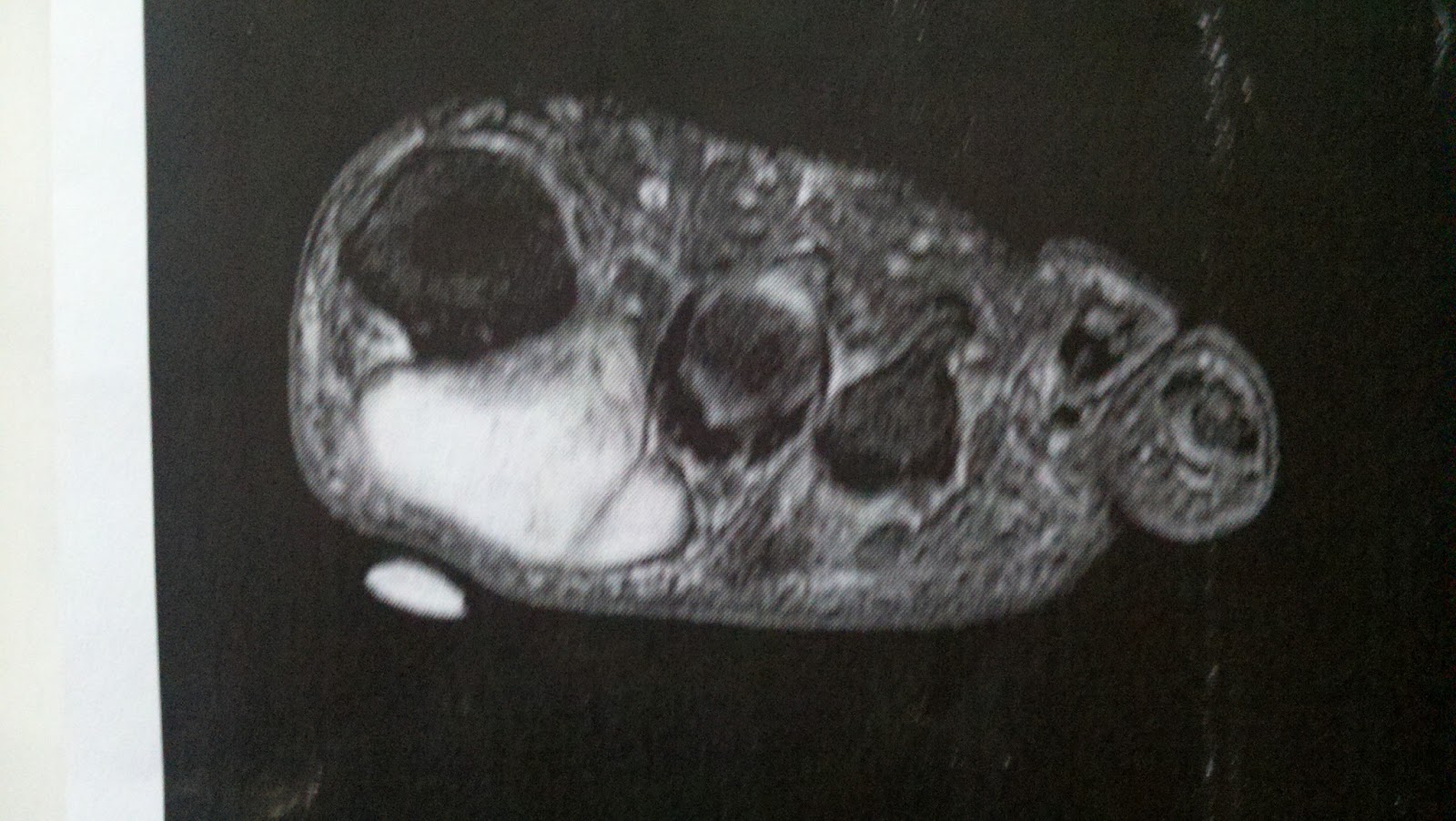
Surgical Treatment
The above measures are often sufficient to resolve Morton?s Neuroma. Should the condition persist or worsen despite these efforts, surgery may be recommended to remove the Neuroma. The surgery requires only a short recovery period, though permanent numbness in the affected toes can result, so such surgery is generally used as a last resort.
Prevention
Although the exact causes of neuromas are not completely known, the following preventive steps may help. Make sure your exercise shoes have enough room in the front part of the shoe and that your toes are not excessively compressed. Wear shoes with adequate padding in the ball of the foot. Avoid prolonged time in shoes with a narrow toe box or excessive heel height (greater than two inches).
 Morton?s neuroma is inflammation, thickening, or enlargement of the nerve between the bones of the toes (metatarsal bones). The condition is also called intermetatarsal neuroma. The thickening is usually found between bones of the third and fourth toes of the foot, but sometimes it may develop between the second and third toes. It occurs when the medial plantar nerve near the bones of those toes becomes compressed or irritated, possibly because the metatarsal bones press against the nerve in the narrow gap between the toes. If left untreated, Morton?s neuroma can cause a sharp, burning, or shooting pain that often gets worse over time. The pain becomes worse when a person walks or stands on the ball of the foot. Sometimes the pain reaches the toes next to the neuroma and a sensation of tingling or numbness is felt.
Morton?s neuroma is inflammation, thickening, or enlargement of the nerve between the bones of the toes (metatarsal bones). The condition is also called intermetatarsal neuroma. The thickening is usually found between bones of the third and fourth toes of the foot, but sometimes it may develop between the second and third toes. It occurs when the medial plantar nerve near the bones of those toes becomes compressed or irritated, possibly because the metatarsal bones press against the nerve in the narrow gap between the toes. If left untreated, Morton?s neuroma can cause a sharp, burning, or shooting pain that often gets worse over time. The pain becomes worse when a person walks or stands on the ball of the foot. Sometimes the pain reaches the toes next to the neuroma and a sensation of tingling or numbness is felt.Causes
A Morton's neuroma commonly occurs due to repetitive weight bearing activity (such as walking or running) particularly when combined with tight fitting shoes or excessive pronation of the feet (i.e. "flat-feet"). The condition is also more common in patients with an unstable forefoot allowing excessive movement between the metatarsal bones. A Morton's neuroma can also occur due to certain foot deformities, trauma to the foot, or the presence of a ganglion or inflamed bursa in the region which may place compressive forces on the nerve.
Symptoms
Symptoms associated with a neuroma include a dull burning sensation radiating towards the toes, a cramping feeling, or even a stinging, tingling sensation that can be described as being similar to an electric shock. It is often worse when wearing shoes with most people finding the pain disappears when removing their shoes.
Diagnosis
To diagnose Morton's neuroma the podiatrist commonly palpates the area to elicit pain, squeezing the toes from the side. Next he or she may try to feel the neuroma by pressing a thumb into the third interspace. The podiatrist then tries to elicit Mulder's sign, by palpating the affected interspace with one hand and squeezing the entire foot at the same time with the other hand. In many cases of Morton's neuroma, this causes an audible click, known as Mulder's sign. An x-ray should be taken to ensure that there is not a fracture. X-rays also can be used to examine the joints and bone density, ruling out arthritis (particularly rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis).
Non Surgical Treatment
Sclerosing alcohol injections are an increasingly available treatment alternative if the above management approaches fail. Dilute alcohol (4%) is injected directly into the area of the neuroma, causing toxicity to the fibrous nerve tissue. Frequently, treatment must be performed 2-4 times, with 1-3 weeks between interventions. An 60-80% success rate has been achieved in clinical studies, equal to or exceeding the success rate for surgical neurectomy with fewer risks and less significant recovery. If done with more concentrated alcohol under ultrasound guidance, the success rate is considerably higher and fewer repeat procedures are needed. Radio Frequency Ablation is also used in the treatment of Morton's Neuroma The outcomes appear to be equally or more reliable than alcohol injections especially if the procedure is done under ultrasound guidance.

Surgical Treatment
The above measures are often sufficient to resolve Morton?s Neuroma. Should the condition persist or worsen despite these efforts, surgery may be recommended to remove the Neuroma. The surgery requires only a short recovery period, though permanent numbness in the affected toes can result, so such surgery is generally used as a last resort.
Prevention
Although the exact causes of neuromas are not completely known, the following preventive steps may help. Make sure your exercise shoes have enough room in the front part of the shoe and that your toes are not excessively compressed. Wear shoes with adequate padding in the ball of the foot. Avoid prolonged time in shoes with a narrow toe box or excessive heel height (greater than two inches).