What Are The Key Causes Of Adult Aquired Flat Foot ?
Overview
Over 60 Million Americans suffer from Adult Acquired Flatfoot (AAF), otherwise known as Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction or PTTD. This condition generally occurs in adults from 40-65 years of age, and it usually only occurs in one foot, not both. The Posterior Tibial (PT) Tendon courses along the inside part of the ankle and underneath the arch of the foot. It is the major supporting structure for the arch. Over time, the tendon becomes diseased, from overuse, and starts to lose it's strength. As a result, the arch begins to collapse, placing further strain on the PT Tendon, leading to further decrease in tendon strength, which causes further collapse of the arch. This is described as a progressive deformity because it will generally get worse over time.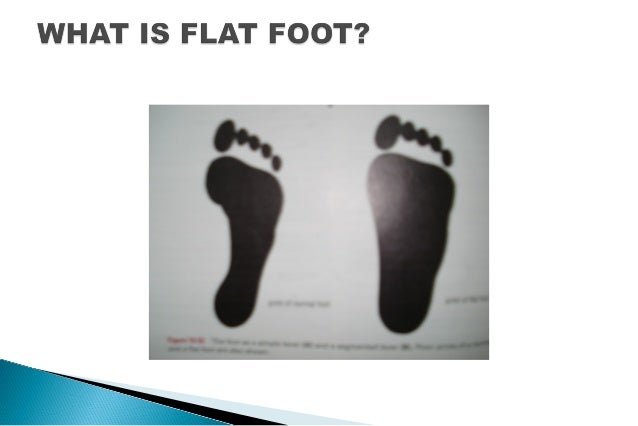
Causes
Causes of an adult acquired flatfoot may include Neuropathic foot (Charcot foot) secondary to Diabetes mellitus, Leprosy, Profound peripheral neuritis of any cause. Degenerative changes in the ankle, talonavicular or tarsometatarsal joints, or both, secondary to Inflammatory arthropathy, Osteoarthropathy, Fractures, Acquired flatfoot resulting from loss of the supporting structures of the medial longitudinal arch. Dysfunction of the tibialis posterior tendon Tear of the spring (calcaneoanvicular) ligament (rare). Tibialis anterior rupture (rare). Painful flatfoot can have other causes, such as tarsal coalition, but as such a patient will not present with a change in the shape of the foot these are not included here.
Symptoms
Some symptoms of adult acquired flat foot are pain along the inside of the foot and ankle, pain that increases with activity, and difficulty walking for long periods of time. You may experience difficulty standing, pain on the outside of the ankle, and bony bumps on the top of the foot and inside the foot. You may also have numbness and tingling of the feet and toes (may result from large bone spurs putting pressure on nerves), swelling, a large bump on the sole of the foot and/or an ulcer (in diabetic patients). Diabetic patients should wear a properly fitting diabetic shoe wear to prevent these complications from happening.
Diagnosis
In the early stages of dysfunction of the posterior tibial tendon, most of the discomfort is located medially along the course of the tendon and the patient reports fatigue and aching on the plantar-medial aspect of the foot and ankle. Swelling is common if the dysfunction is associated with tenosynovitis. As dysfunction of the tendon progresses, maximum pain occurs laterally in the sinus tarsi because of impingement of the fibula against the calcaneus. With increasing deformity, patients report that the shape of the foot changes and that it becomes increasingly difficult to wear shoes. Many patients no longer report pain in the medial part of the foot and ankle after a complete rupture of the posterior tibial tendon has occurred; instead, the pain is located laterally. If a fixed deformity has not occurred, the patient may report that standing or walking with the hindfoot slightly inverted alleviates the lateral impingement and relieves the pain in the lateral part of the foot.
Non surgical Treatment
Initial treatment is based on the degree of deformity and flexibility at initial presentation. Conservative treatment includes orthotics or ankle foot orthoses (AFO) to support the posterior tibial tendon (PT) and the longitudinal arch, anti-inflammatories to help reduce pain and inflammation, activity modification which may include immobilization of the foot and physical therapy to help strengthen and rehabilitate the tendon.

Surgical Treatment
Surgical treatment should be considered when all other conservative treatment has failed. Surgery options for flatfoot reconstruction depend on the severity of the flatfoot. Surgery for a flexible flatfoot deformity (flatfoot without arthritis to the foot joints) involves advancing the posterior tibial tendon under the arch to provide more support and decrease elongation of the tendon as well as addressing the hindfoot eversion with a osteotomy to the calcaneus (surgical cut in the heel bone). Additionally, the Achilles tendon may need to be lengthened because of the compensatory contracture of the Achilles tendon with flatfoot deformity. Flatfoot deformity with arthritic changes to the foot is considered a rigid flatfoot. Correction of a rigid flatfoot deformity usually involves surgical fusion of the hindfoot joints. This is a reconstructive procedure which allows the surgeon to re-position the foot into a normal position. Although the procedure should be considered for advanced PTTD, it has many complications and should be discussed at length with your doctor.
Over 60 Million Americans suffer from Adult Acquired Flatfoot (AAF), otherwise known as Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction or PTTD. This condition generally occurs in adults from 40-65 years of age, and it usually only occurs in one foot, not both. The Posterior Tibial (PT) Tendon courses along the inside part of the ankle and underneath the arch of the foot. It is the major supporting structure for the arch. Over time, the tendon becomes diseased, from overuse, and starts to lose it's strength. As a result, the arch begins to collapse, placing further strain on the PT Tendon, leading to further decrease in tendon strength, which causes further collapse of the arch. This is described as a progressive deformity because it will generally get worse over time.

Causes
Causes of an adult acquired flatfoot may include Neuropathic foot (Charcot foot) secondary to Diabetes mellitus, Leprosy, Profound peripheral neuritis of any cause. Degenerative changes in the ankle, talonavicular or tarsometatarsal joints, or both, secondary to Inflammatory arthropathy, Osteoarthropathy, Fractures, Acquired flatfoot resulting from loss of the supporting structures of the medial longitudinal arch. Dysfunction of the tibialis posterior tendon Tear of the spring (calcaneoanvicular) ligament (rare). Tibialis anterior rupture (rare). Painful flatfoot can have other causes, such as tarsal coalition, but as such a patient will not present with a change in the shape of the foot these are not included here.
Symptoms
Some symptoms of adult acquired flat foot are pain along the inside of the foot and ankle, pain that increases with activity, and difficulty walking for long periods of time. You may experience difficulty standing, pain on the outside of the ankle, and bony bumps on the top of the foot and inside the foot. You may also have numbness and tingling of the feet and toes (may result from large bone spurs putting pressure on nerves), swelling, a large bump on the sole of the foot and/or an ulcer (in diabetic patients). Diabetic patients should wear a properly fitting diabetic shoe wear to prevent these complications from happening.
Diagnosis
In the early stages of dysfunction of the posterior tibial tendon, most of the discomfort is located medially along the course of the tendon and the patient reports fatigue and aching on the plantar-medial aspect of the foot and ankle. Swelling is common if the dysfunction is associated with tenosynovitis. As dysfunction of the tendon progresses, maximum pain occurs laterally in the sinus tarsi because of impingement of the fibula against the calcaneus. With increasing deformity, patients report that the shape of the foot changes and that it becomes increasingly difficult to wear shoes. Many patients no longer report pain in the medial part of the foot and ankle after a complete rupture of the posterior tibial tendon has occurred; instead, the pain is located laterally. If a fixed deformity has not occurred, the patient may report that standing or walking with the hindfoot slightly inverted alleviates the lateral impingement and relieves the pain in the lateral part of the foot.
Non surgical Treatment
Initial treatment is based on the degree of deformity and flexibility at initial presentation. Conservative treatment includes orthotics or ankle foot orthoses (AFO) to support the posterior tibial tendon (PT) and the longitudinal arch, anti-inflammatories to help reduce pain and inflammation, activity modification which may include immobilization of the foot and physical therapy to help strengthen and rehabilitate the tendon.

Surgical Treatment
Surgical treatment should be considered when all other conservative treatment has failed. Surgery options for flatfoot reconstruction depend on the severity of the flatfoot. Surgery for a flexible flatfoot deformity (flatfoot without arthritis to the foot joints) involves advancing the posterior tibial tendon under the arch to provide more support and decrease elongation of the tendon as well as addressing the hindfoot eversion with a osteotomy to the calcaneus (surgical cut in the heel bone). Additionally, the Achilles tendon may need to be lengthened because of the compensatory contracture of the Achilles tendon with flatfoot deformity. Flatfoot deformity with arthritic changes to the foot is considered a rigid flatfoot. Correction of a rigid flatfoot deformity usually involves surgical fusion of the hindfoot joints. This is a reconstructive procedure which allows the surgeon to re-position the foot into a normal position. Although the procedure should be considered for advanced PTTD, it has many complications and should be discussed at length with your doctor.
Achilles Tendon Pain
Overview
 Typically an overuse injury, Achilles tendinitis affects the connective tissue between the calf and the heel. When you walk, run or otherwise use your leg to push your body upward, the Achilles tendon is engaged. Using the tendon frequently and with high intensity often results in tendinitis -- a swollen Achilles tendon that makes it difficult and sometimes painful to continue high-impact activities.
Typically an overuse injury, Achilles tendinitis affects the connective tissue between the calf and the heel. When you walk, run or otherwise use your leg to push your body upward, the Achilles tendon is engaged. Using the tendon frequently and with high intensity often results in tendinitis -- a swollen Achilles tendon that makes it difficult and sometimes painful to continue high-impact activities.
Causes
The majority of Achilles tendon injuries are due to overuse injuries. Other factors that lead to Achilles tendonitis are improper shoe selection, inadequate stretching prior to engaging in athletics, a short Achilles tendon, direct trauma (injury) to the tendon, training errors and heel bone deformity. There is significant evidence that people with feet that role in excessively (over-pronate) are at greater risk for developing Achilles tendinitis. The increased pronation puts additional stress on the tendon, therefore, placing it at greater risk for injury.
Symptoms
Paratenonitis presents in younger people. Symptoms start gradually and spontaneously. Aching and burning pain is noted especially with morning activity. It may improve slightly with initial activity, but becomes worse with further activity. It is aggravated by exercise. Over time less exercise is required to cause the pain. The Achilles tendon is often enlarged, warm and tender approximately 1 to 4 inches above its heel insertion. Sometimes friction is noted with gentle palpation of the tendon during ankle motion. Tendinosis presents similarly but typically in middle-aged people. If severe pain and limited walking ability are present, it may indicate a partial tear of the tendon.
Diagnosis
During an examination of the foot and ankle, you doctor will look for the following signs, Achilles tendon swelling or thickening. Bone spurs appearing at the lower part of the tendon at the back of the hell. Pain at the middle or lower area of the Achilles tendon. Limited range of motion of the foot and ankle, and a decreased ability to flex the foot. Your doctor may perform imaging tests, such as X-rays and MRI scans, to make a diagnosis of Achilles tendinitis. X-rays show images of the bones and can help the physician to determine if the Achilles tendon has become hardened, which indicated insertional Achilles tendinitis. MRI scans may not be necessary, but they are important guides if you are recommended to have surgical treatment. An MRI can show the severity of the damage and determine what kind of procedure would be best to address the condition.
Nonsurgical Treatment
Treatment will focus on relieving the pain and preventing further injury. Your podiatrist may create shoe inserts or a soft cast to effectively immobilize the affected area for a period of time. (Often, a couple of weeks are needed for the tendon to heal.) Medication can help too. Your podiatrist may recommend or prescribe oral medication.

Surgical Treatment
Surgery usually isn't needed to treat Achilles tendinopathy. But in rare cases, someone might consider surgery when rubbing between the tendon and the tissue covering the tendon (tendon sheath) causes the sheath to become thick and fibrous. Surgery can be done to remove the fibrous tissue and repair any small tendon tears. This may also help prevent an Achilles tendon rupture.
Prevention
Your podiatrist will work with you to decrease your chances of re-developing tendinitis. He or she may create custom orthotics to help control the motion of your feet. He or she may also recommend certain stretches or exercises to increase the tendon's elasticity and strengthen the muscles attached to the tendon. Gradually increasing your activity level with an appropriate training schedule-building up to a 5K run, for instance, instead of simply tackling the whole course the first day-can also help prevent tendinitis.
 Typically an overuse injury, Achilles tendinitis affects the connective tissue between the calf and the heel. When you walk, run or otherwise use your leg to push your body upward, the Achilles tendon is engaged. Using the tendon frequently and with high intensity often results in tendinitis -- a swollen Achilles tendon that makes it difficult and sometimes painful to continue high-impact activities.
Typically an overuse injury, Achilles tendinitis affects the connective tissue between the calf and the heel. When you walk, run or otherwise use your leg to push your body upward, the Achilles tendon is engaged. Using the tendon frequently and with high intensity often results in tendinitis -- a swollen Achilles tendon that makes it difficult and sometimes painful to continue high-impact activities.
Causes
The majority of Achilles tendon injuries are due to overuse injuries. Other factors that lead to Achilles tendonitis are improper shoe selection, inadequate stretching prior to engaging in athletics, a short Achilles tendon, direct trauma (injury) to the tendon, training errors and heel bone deformity. There is significant evidence that people with feet that role in excessively (over-pronate) are at greater risk for developing Achilles tendinitis. The increased pronation puts additional stress on the tendon, therefore, placing it at greater risk for injury.
Symptoms
Paratenonitis presents in younger people. Symptoms start gradually and spontaneously. Aching and burning pain is noted especially with morning activity. It may improve slightly with initial activity, but becomes worse with further activity. It is aggravated by exercise. Over time less exercise is required to cause the pain. The Achilles tendon is often enlarged, warm and tender approximately 1 to 4 inches above its heel insertion. Sometimes friction is noted with gentle palpation of the tendon during ankle motion. Tendinosis presents similarly but typically in middle-aged people. If severe pain and limited walking ability are present, it may indicate a partial tear of the tendon.
Diagnosis
During an examination of the foot and ankle, you doctor will look for the following signs, Achilles tendon swelling or thickening. Bone spurs appearing at the lower part of the tendon at the back of the hell. Pain at the middle or lower area of the Achilles tendon. Limited range of motion of the foot and ankle, and a decreased ability to flex the foot. Your doctor may perform imaging tests, such as X-rays and MRI scans, to make a diagnosis of Achilles tendinitis. X-rays show images of the bones and can help the physician to determine if the Achilles tendon has become hardened, which indicated insertional Achilles tendinitis. MRI scans may not be necessary, but they are important guides if you are recommended to have surgical treatment. An MRI can show the severity of the damage and determine what kind of procedure would be best to address the condition.
Nonsurgical Treatment
Treatment will focus on relieving the pain and preventing further injury. Your podiatrist may create shoe inserts or a soft cast to effectively immobilize the affected area for a period of time. (Often, a couple of weeks are needed for the tendon to heal.) Medication can help too. Your podiatrist may recommend or prescribe oral medication.

Surgical Treatment
Surgery usually isn't needed to treat Achilles tendinopathy. But in rare cases, someone might consider surgery when rubbing between the tendon and the tissue covering the tendon (tendon sheath) causes the sheath to become thick and fibrous. Surgery can be done to remove the fibrous tissue and repair any small tendon tears. This may also help prevent an Achilles tendon rupture.
Prevention
Your podiatrist will work with you to decrease your chances of re-developing tendinitis. He or she may create custom orthotics to help control the motion of your feet. He or she may also recommend certain stretches or exercises to increase the tendon's elasticity and strengthen the muscles attached to the tendon. Gradually increasing your activity level with an appropriate training schedule-building up to a 5K run, for instance, instead of simply tackling the whole course the first day-can also help prevent tendinitis.
What Triggers Painful Heel To Appear

Overview
Plantar fasciitis causes pain under your heel. It usually goes in time. Treatment may speed up recovery. Treatment includes rest, good footwear, heel pads, painkillers, and exercises. A steroid injection or other treatments may be used in more severe cases. Plantar fasciitis means inflammation of your plantar fascia. Your plantar fascia is a strong band of tissue (like a ligament) that stretches from your heel to your middle foot bones. It supports the arch of your foot and also acts as a shock-absorber in your foot.
Causes
The most common cause of plantar fasciitis relates to faulty structure of the foot. For example, people who have problems with their arches, either overly flat feet or high-arched feet, are more prone to developing plantar fasciitis. Wearing non-supportive footwear on hard, flat surfaces puts abnormal strain on the plantar fascia and can also lead to plantar fasciitis. This is particularly evident when one’s job requires long hours on the feet. Obesity may also contribute to plantar fasciitis.
Symptoms
The condition typically starts gradually with mild pain at the heel bone often referred to as a stone bruise. You're more likely to feel it after (not during) exercise. The pain classically occurs right after getting up in the morning and after a period of sitting. If you don't treat plantar fasciitis, it may become a chronic condition. You may not be able to keep up your level of activity, and you may develop symptoms of foot, knee, hip and back problems because plantar fasciitis can change the way you walk.
Diagnosis
A health care professional will ask you whether you have the classic symptoms of first-step pain and about your activities, including whether you recently have intensified your training or changed your exercise pattern. Your doctor often can diagnose plantar fasciitis based on your history and symptoms, together with a physical examination. If the diagnosis is in doubt, your doctor may order a foot X-ray, bone scan or nerve conduction studies to rule out another condition, such as a stress fracture or nerve problem.
Non Surgical Treatment
Anti-inflammatory medications can help decrease the inflammation in the arch and heel of your foot. These medications include Advil, Mtrin, Ibuprofen, and Aleve. Use the medication as directed on the package. If you tolerate it well, take it daily for two weeks then discontinue for one week. If symptoms worsen or return, resume for two weeks, then stop. You should eat when taking these medications, as they can be hard on your stomach. Ach Support. Over the counter inserts provide added arch support and soft cushion. Based on the individual needs of your foot, you may require custom inserts. Achilles Tendon Stretch. Pace a shoe insert under your affected foot. Place your affected leg behind your unaffected leg with the toes of your back foot pointed towards the heel of your other foot. Lean into the wall. Bend your front knee while keeping your back leg straight with your heel firmly on the ground. Hold the stretch for a count of 10. A set is 10 repetitions. Perform the stretch at least three times a day.

Surgical Treatment
If treatment hasn't worked and you still have painful symptoms after a year, your GP may refer you to either an orthopaedic surgeon, a surgeon who specialises in surgery that involves bones, muscles and joints, a podiatric surgeon, a podiatrist who specialises in foot surgery. Surgery is sometimes recommended for professional athletes and other sportspeople whose heel pain is adversely affecting their career. Plantar release surgery. Plantar release surgery is the most widely used type of surgery for heel pain. The surgeon will cut the fascia to release it from your heel bone and reduce the tension in your plantar fascia. This should reduce any inflammation and relieve your painful symptoms. Surgery can be performed either as, open surgery, where the section of the plantar fascia is released by making a cut into your heel, endoscopic or minimal incision surgery - where a smaller incision is made and special instruments are inserted through the incision to gain access to the plantar fascia. Endoscopic or minimal incision surgery has a quicker recovery time, so you will be able to walk normally much sooner (almost immediately), compared with two to three weeks for open surgery. A disadvantage of endoscopic surgery is that it requires both a specially trained surgical team and specialised equipment, so you may have to wait longer for treatment than if you were to choose open surgery. Endoscopic surgery also carries a higher risk of damaging nearby nerves, which could result in symptoms such as numbness, tingling or some loss of movement in your foot. As with all surgery, plantar release carries the risk of causing complications such as infection, nerve damage and a worsening of your symptoms after surgery (although this is rare). You should discuss the advantages and disadvantages of both techniques with your surgical team. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (EST) is a fairly new type of non-invasive treatment. Non-invasive means it does not involve making cuts into your body. EST involves using a device to deliver high-energy soundwaves into your heel. The soundwaves can sometimes cause pain, so a local anaesthetic may be used to numb your heel. It is claimed that EST works in two ways. It is thought to, have a "numbing" effect on the nerves that transmit pain signals to your brain, help stimulate and speed up the healing process. However, these claims have not yet been definitively proven. The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) has issued guidance about the use of EST for treating plantar fasciitis. NICE states there are no concerns over the safety of EST, but there are uncertainties about how effective the procedure is for treating heel pain. Some studies have reported that EST is more effective than surgery and other non-surgical treatments, while other studies found the procedure to be no better than a placebo (sham treatment).
Stretching Exercises
The following exercises are commonly prescribed to patients with this condition. You should discuss the suitability of these exercises with your physiotherapist prior to beginning them. Generally, they should be performed 2 - 3 times daily and only provided they do not cause or increase symptoms. Your physiotherapist can advise when it is appropriate to begin the initial exercises and eventually progress to the intermediate and advanced exercises. As a general rule, addition of exercises or progression to more advanced exercises should take place provided there is no increase in symptoms. Calf Stretch with Towel. Begin this stretch in long sitting with your leg to be stretched in front of you. Your knee and back should be straight and a towel or rigid band placed around your foot as demonstrated. Using your foot, ankle and the towel, bring your toes towards your head until you feel a stretch in the back of your calf, Achilles tendon, plantar fascia or leg. Hold for 5 seconds and repeat 10 times at a mild to moderate stretch provided the exercise is pain free. Resistance Band Calf Strengthening. Begin this exercise with a resistance band around your foot as demonstrated and your foot and ankle held up towards your head. Slowly move your foot and ankle down against the resistance band as far as possible and comfortable without pain, tightening your calf muscle. Very slowly return back to the starting position. Repeat 10 - 20 times provided the exercise is pain free.
What Is Pain On The Heel

Overview
Plantar fasciitis is a common cause of heel pain in adults. The disorder classically presents with pain that is particularly severe with the first few steps taken in the morning. In general, plantar fasciitis is a self-limited condition. However, symptoms usually resolve more quickly when the interval between the onset of symptoms and the onset of treatment is shorter. Many treatment options exist, including rest, stretching, strengthening, change of shoes, arch supports, orthotics, night splints, anti-inflammatory agents and surgery. Usually, plantar fasciitis can be treated successfully by tailoring treatment to an individual's risk factors and preferences.
Causes
When some people stand/walk/run/jump their own anatomy in their ankle joint is not ‘sturdy’ enough to cope with the needed stabilisation of their ankle joint when they are weight bearing. So, their ankle rotates to find a point of stability. By the shin twisting in and the ankle rotating downwards to the inside (along with your body weight, the power of some muscles, and of course, gravity) a huge amount of stress is applied to the plantar fascia until it is stressed beyond it’s normal limits and it starts to ‘tighten up’. It is this tightening up of the plantar fascia under this stress that causes the damage that in turn leads to pain…eventually.
Symptoms
The major complaint of those with plantar fasciitis is pain and stiffness in the bottom of the heel. This develops gradually over time. It usually affects just one foot, but can affect both feet. Some people describe the pain as dull, while others experience a sharp pain, and some feel a burning or ache on the bottom of the foot extending outward from the heel. The pain is usually worse in the morning when you take your first steps out of bed, or if you’ve been sitting or lying down for a while. Climbing stairs can be very difficult due to the heel stiffness. After prolonged activity, the pain can flare-up due to increased inflammation. Pain is not usually felt during the activity, but rather just after stopping.
Diagnosis
Most cases of plantar fasciitis are diagnosed by a health care provider who listens carefully to your description of symptoms. During an examination of your feet, your health care provider will have to press on the bottom of your feet, the area most likely to be painful in plantar fasciitis. Because the pain of plantar fasciitis has unique characteristics, pain upon rising, improvement after walking for several minutes, pain produced by pressure applied in a specific location on your foot but not with pressure in other areas, your health care provider will probably feel comfortable making the diagnosis based on your symptoms and a physical examination. Your health care provider may suggest that you have an X-ray of your foot to verify that there is no stress fracture causing your pain.
Non Surgical Treatment
The key for the proper treatment of plantar fasciitis is determining what is causing the excessive stretching of the plantar fascia. When the cause is over-pronation (flat feet), an orthotic with rearfoot posting and longitudinal arch support is an effective device to reduce the over-pronation and allow the condition to heal. If you have usually high arches, which can also lead to plantar fasciitis, cushion the heel, absorb shock and wear proper footwear that will accommodate and comfort the foot. Other common treatments include stretching exercises, plantar fasciitis night splints, wearing shoes that have a cushioned heel to absorb shock, and elevating the heel with the use of a heel cradle or heel cup. Heel cradles and heel cups provide extra comfort, cushion the heel, and reduce the amount of shock and shear forces placed during everyday activities.

Surgical Treatment
Surgery is usually not needed for plantar fasciitis. About 95 out of 100 people who have plantar fasciitis are able to relieve heel pain without surgery. Your doctor may consider surgery if non-surgical treatment has not helped and heel pain is restricting your daily activities. Some doctors feel that you should try non-surgical treatment for at least 6 months before you consider surgery. The main types of surgery for plantar fasciitis are Plantar fascia release. This procedure involves cutting part of the plantar fascia ligament . This releases the tension on the ligament and relieves inflammation . Other procedures, such as removing a heel spur or stretching or loosening specific foot nerves. These surgeries are usually done in combination with plantar fascia release when there is lasting heel pain and another heel problem. Experts in the past thought that heel spurs caused plantar fasciitis. Now experts generally believe that heel spurs are the result, not the cause, of plantar fasciitis. Many people with large heel spurs never have heel pain or plantar fasciitis. So surgery to remove heel spurs is rarely done.
Stretching Exercises
Stretching exercises for your foot are important. Do the stretches shown here at least twice a day. Don't bounce when you stretch. Plantar fascia stretch. To do the plantar fascia stretch, stand straight with your hands against a wall and your injured leg slightly behind your other leg. Keeping your heels flat on the floor, slowly bend both knees. You should feel the stretch in the lower part of your leg. Hold the stretch for 10 to 15 seconds. Repeat the stretch 6 to 8 times. Calf stretch. Stand with your hands against a wall and your injured leg behind your other leg. With your injured leg straight, your heel flat on the floor and your foot pointed straight ahead, lean slowly forward, bending the other leg. You should feel the stretch in the middle of your calf. Hold the stretch for 10 to 15 seconds. Repeat the stretch 6 to 8 times. Other exercises. You can also strengthen your leg muscles by standing on the ball of your foot at the edge of a step and raising up as high as possible on your toes. Relax between toe raises and let your heel fall a little lower than the edge of the step. It's also helpful to strengthen the foot by grabbing a towel with your toes as if you are going to pick up the towel with your foot. Repeat this exercise several times a day.
What Causes Heel Discomfort To Appear

Overview
Plantar Fasciitis is the Latin term for "inflammation of the plantar fascia". The plantar fascia is a thick, fibrous ligament that runs under the foot from the heel bone to the toes. It forms the arch of the foot and functions as our natural shock-absorbing mechanism. Unlike muscle tissue, the plantar fascia is not very elastic and therefore is very limited in its capacity to stretch or elongate. Herein lies the problem, when too much traction is placed on the plantar fascia (for various reasons) micro-tearing will occur, resulting in irritation, inflammation and pain. Plantar Fasciitis usually causes pain under the heel. However some people may experience pain under the arch of the foot. Both heel pain and arch discomfort are related to Plantar Fasciitis, with heel pain being far more common than arch pain.
Causes
You are at a greater risk for developing plantar fasciitis if you are overweight or obese. This is due to the increased pressure on your plantar fascia ligaments, especially if you have sudden weight gain. Women who are pregnant often experience bouts of plantar fasciitis, particularly during late pregnancy. If you are a long distance runner, you may be more likely to develop plantar fascia problems. You are also at risk if you have a very active job that involves being on your feet often, such as a factory worker or a restaurant server. Active men and women between the ages of 40 and 70 are at the highest risk for developing plantar fasciitis. It is also slightly more common in women than men. If you have foot problems, such as very high arches or very flat feet, you may develop plantar fasciitis. Tight Achilles tendons (the tendons attaching the calf muscles to the heels) may also result in plantar fascia pain. Simply wearing shoes with soft soles and poor arch support can also result in plantar fasciitis. Plantar fasciitis is not caused by heel spurs. A heel spur is a hook of bone that can form on the heel bone (calcaneus) of the foot. One out of every 10 people has a heel spur, but only one out of 20 people with heel spurs experience pain, according to OrthoInfo.
Symptoms
The typical presentation is sharp pain localized at the anterior aspect of the calcaneus. Plantar fasciitis has a partial association with a heel spur (exostosis); however, many asymptomatic individuals have bony heel spurs, whereas many patients with plantar fasciitis do not have a spur.
Diagnosis
Plantar fasciitis is one of many conditions causing "heel pain". Some other possible causes include nerve compression either in the foot or in the back, stress fracture of the calcaneus, and loss of the fatty tissue pad under the heel. Plantar fasciitis can be distinguished from these and other conditions based on a history and examination done by a physician. It should be noted that heel spurs are often inappropriately thought to be the sole cause of heel pain. In fact, heel spurs are common and are nothing more than the bone's response to traction or pulling-type forces from the plantar fascia and other muscles in the foot where they attach to the heel bone. They are commonly present in patients without pain, and frequently absent from those who have pain. It is the rare patient who has a truly enlarged and problematic spur requiring surgery.
Non Surgical Treatment
In general, we start by correcting training errors. This usually requires relative rest, the use of ice after activities, and an evaluation of the patient's shoes and activities. Next, we try correction of biomechanical factors with a stretching and strengthening program. If the patient still has no improvement, we consider night splints and orthotics. Finally, all other treatment options are considered. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications are considered throughout the treatment course, although we explain to the patient that this medicine is being used primarily for pain control and not to treat the underlying problem.

Surgical Treatment
Most studies indicate that 95% of those afflicted with plantar fasciitis are able to relieve their heel pain with nonsurgical treatments. If you are one of the few people whose symptoms don't improve with other treatments, your doctor may recommend plantar fascia release surgery. Plantar fascia release involves cutting part of the plantar fascia ligament in order to release the tension and relieve the inflammation of the ligament. Overall, the success rate of surgical release is 70 to 90 percent in patients with plantar fasciitis. While the success rate is very high following surgery, one should be aware that there is often a prolonged postoperative period of discomfort similar to the discomfort experienced prior to surgery. This pain usually will abate within 2-3 months. One should always be sure to understand all the risks associated with any surgery they are considering.
Prevention
Stretching the plantar fascia and the calf muscle area can help to prevent inflammation. Slowly increasing the amount or intensity of athletic activities by graded progression can also help to prevent injury. Recommended Stretches: Taking a lunge position with the injured foot behind and keeping your heels flat on the floor, lean into a wall and bend the knees. A stretch should be felt in the sole and in the Achilles tendon area. Hold the stretch for 20-30 seconds. Also try this stretch with the back leg straight.
What Triggers Heel Pain To Flare Up

Overview
Plantar fasciitis is one of the most common causes of heel pain. It involves pain and inflammation of a thick band of tissue, called the plantar fascia, that runs across the bottom of your foot and connects your heel bone to your toes. Plantar fasciitis commonly causes stabbing pain that usually occurs with your very first steps in the morning. Once your foot limbers up, the pain of plantar fasciitis normally decreases, but it may return after long periods of standing or after getting up from a seated position. Plantar fasciitis is particularly common in runners. In addition, people who are overweight and those who wear shoes with inadequate support are at risk of plantar fasciitis.
Causes
Plantar fasciitis is the most common cause of heel pain, accounting for around four out of five cases. Plantar fasciitis is when the thick band of tissue that connects the heel bone with the rest of the foot (the plantar fascia) becomes damaged and thickened. Damage to the plantar fascia is thought to occur following sudden damage, for example, damaging your heel while jogging, running or dancing; this type of damage usually affects younger people who are physically active, gradual wear and tear of the tissues that make up the plantar fascia - this usually affects adults who are 40 years of age or over. You are at an increased risk of gradual wear and tear damaging your plantar fasciitis if you are overweight or obese, if you have a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or over, you are considered to be obese, have a job that involves spending long periods of time standing, wear flat-soled shoes, such as sandals or flip flops. Less common causes of heel pain are a stress fracture. A stress fracture can occur if your heel bone is damaged during an injury. Fat pad atrophy. Fat pad atrophy is where the layer of fat that lies under the heel bone, known as the fat pad, starts to waste away due to too much strain being placed on the pad. Women who wear high-heeled shoes for many years have an increased risk of developing fat pad atrophy. Bursitis. Bursitis is inflammation of one or more bursa (small fluid-filled sacs under the skin, usually found over the joints and between tendons and bones). It's possible to develop bursitis anywhere inside the body, not just in the foot. Tarsal tunnel syndrome. The nerves in the sole of your foot pass through a small tunnel on the inside of the ankle joint, known as the tarsal tunnel. If a cyst forms or the tunnel is damaged, the nerves can become compressed (squashed). This can cause pain anywhere along the nerve, including beneath your heel. Sever's disease. Sever's disease is a common cause of heel pain in children. It's caused by the muscles and tendons of the hamstrings and calves stretching and tightening in response to growth spurts. The stretching of the calf muscle pulls on the Achilles tendon. This pulls on the growing area of bone at the back of the heel (growth plate), causing pain in the heel. The pain is further aggravated by activities such as football and gymnastics. The pain often develops at the side of the heel, but can also be felt under the heel. Calf and hamstring stretches and, if necessary, heel pads are usually effective treatments for Sever's disease. Bone spurs. Bone spurs are an excess growth of bone that forms on a normal bone. Bone spurs can develop on the heel (a heel spur) and are more common in people with heel pain. However, they can also occur in people without heel pain. A heel spur does not cause heel pain.
Symptoms
People with this condition sometimes describe the feeling as a hot, sharp sensation in the heel. You usually notice the pain first thing in the morning when you stand. After walking for a period of time, the pain usually lessens or even disappears. However, sharp pain in the center of the heel may return after resting for a period of time and then resuming activity.
Diagnosis
If you see a doctor for heel pain, he or she will first ask questions about where you feel the pain. If plantar fasciitis is suspected, the doctor will ask about what activities you've been doing that might be putting you at risk. The doctor will also examine your foot by pressing on it or asking you to flex it to see if that makes the pain worse. If something else might be causing the pain, like a heel spur or a bone fracture, the doctor may order an X-ray to take a look at the bones of your feet. In rare cases, if heel pain doesn't respond to regular treatments, the doctor also might order an MRI scan of your foot. The good news about plantar fasciitis is that it usually goes away after a few months if you do a few simple things like stretching exercises and cutting back on activities that might have caused the problem. Taking over-the-counter medicines can help with pain. It's rare that people need surgery for plantar fasciitis. Doctors only do surgery as a last resort if nothing else eases the pain.
Non Surgical Treatment
Over-the-counter Orthotics. A soft, over-the-counter orthotic (Prefabricated orthotic) with an accommodating arch support has proven to be quite helpful in the management of plantar fascia symptoms. Studies demonstrate that it is NOT necessary to obtain a custom orthotic for the treatment of this problem. Comfort Shoes. Shoes with a stiff sole, rocker-bottom contour, and a comfortable leather upper combined with an over-the-counter orthotic or a padded heel can be very helpful in the treatment of plantar fasciitis. Anti-Inflammatory Medication (NSAIDs): A short course of over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications may be helpful in managing plantar fasciitis symptoms providing the patient does not have any contra-indications such as a history of stomach ulcers. Activity Modification Any activity that has recently been started, such as a new running routine or a new exercise at the gym that may have increased loading through the heel area, should be stopped on a temporary basis until the symptoms have resolved. At that point, these activities can be gradually started again. Also, any activity changes (ex. sitting more) that will limit the amount of time a patient is on their feet each day may be helpful. A night splint, which keeps the ankle in a neutral position (right angle) while the patient sleeps, can be very helpful in alleviating the significant morning symptoms. A night splint may be prescribed by your physician. Alternatively, it can be ordered online or even obtained in some medical supply stores. This splint is worn nightly for 1-3 weeks until the cycle of pain is broken. Furthermore, this splinting can be reinstituted for a short period of time is symptoms recur.
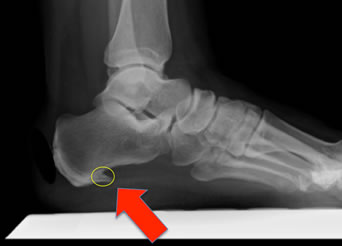
Surgical Treatment
If you consider surgery, your original diagnosis should be confirmed by the surgeon first. In addition, supporting diagnostic evidence (such as nerve-conduction studies) should be gathered to rule out nerve entrapment, particularly of the first branch of the lateral plantar nerve and the medial plantar nerve. Blood tests should consist of an erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), rheumatoid factor, human leukocyte antigen B27 (HLA-B27), and uric acid. It’s important to understand that surgical treatment of bone spurs rarely improves plantar fasciitis pain. And surgery for plantar fasciitis can cause secondary complications-a troubling condition known as lateral column syndrome.
Prevention
Being overweight can place excess pressure and strain on your feet, particularly on your heels. Losing weight, and maintaining a healthy weight by combining regular exercise with a healthy, balanced diet, can be beneficial for your feet. Wearing appropriate footwear is also important. Ideally, you should wear shoes with a low to moderate heel that supports and cushions your arches and heels. Avoid wearing shoes with no heels.
Symptoms Of Compartment Syndrome
Pain across the bottom of the foot at any point between the heel and the ball of the foot is often referred to as "arch pain” Although this description is non-specific, most arch pain is due to strain or inflammation Pes Planus of the plantar fascia (a long ligament on the bottom of the foot). Wearing inappropriate footwear or foot problems like athlete's foot and Morton's neuroma are some of the factors that cause burning feet sensation.
U-Shaped portion surrounds sore callus and reduces pain by transferring pressure from callus to the cushion. Soft orthotics cushion the ball and arches of the feet and protect them from injury and pain, while rigid orthotics correct abnormal foot angles and movements that can cause or worsen pain in the ball of the foot. Many insoles fit inside of slippers so that people suffering from pain in the ball of the foot can walk more comfortably inside their homes as well as outside. In addition, some insoles include added deodorizers to help decrease foot odor. While gel or foam insoles are sold at pharmacies, grocery stores and sporting-goods stores, orthotics require a visit to a podiatrist, who will make a cast of the foot and build a custom-fit insole from the cast. Foam, gel and soft orthotics require replacement once a year or more as the cushioning wears out. Rigid orthotics rarely need replacement. Hip bone spur can cause a lot of discomfort.
Pain often occurs suddenly and mainly around the undersurface of the heel, although it often spreads to your arch. The condition can be temporary, but may become chronic if you ignore it. Resting usually provides relief, but the pain may return. Heel spurs are bony growths that protrude from the bottom of the heel bone, and they are parallel to the ground. There is a nerve that runs very close to this area and may contribute to the pain which occurs.
The spur occurs where the plantar fascia attaches, and the pain in that area is really due to the plantar fascia attachment being irritated. However, there are many people with heel spurs who have no symptoms at all. Haglund's deformity is a bony growth on the back of the heel bone, which then irritates the bursa and the skin lying behind the heel bone. Achilles tendinopathy is degeneration of the tendon that connects your calf muscles to your heel bone. Stress fractures are common in military training.
Went to Podiatrist after receiving pain pills to move, got MRI and he told me I have severe tear in plantor faciitis tendon. Have swelling or what I call a fatty feeling, as I have always had on ball of foot below left most two toes. And it seems to feel a little more fatty since I walked for the first time today after putting on a good pair of ankle boots. Any idea what the fatty feeling is on ball of foot. Lastly, I took the boot off at my stairs into my house 2 days ago and took a step using ball of left foot and it did not pop.
U-Shaped portion surrounds sore callus and reduces pain by transferring pressure from callus to the cushion. Soft orthotics cushion the ball and arches of the feet and protect them from injury and pain, while rigid orthotics correct abnormal foot angles and movements that can cause or worsen pain in the ball of the foot. Many insoles fit inside of slippers so that people suffering from pain in the ball of the foot can walk more comfortably inside their homes as well as outside. In addition, some insoles include added deodorizers to help decrease foot odor. While gel or foam insoles are sold at pharmacies, grocery stores and sporting-goods stores, orthotics require a visit to a podiatrist, who will make a cast of the foot and build a custom-fit insole from the cast. Foam, gel and soft orthotics require replacement once a year or more as the cushioning wears out. Rigid orthotics rarely need replacement. Hip bone spur can cause a lot of discomfort.
Pain often occurs suddenly and mainly around the undersurface of the heel, although it often spreads to your arch. The condition can be temporary, but may become chronic if you ignore it. Resting usually provides relief, but the pain may return. Heel spurs are bony growths that protrude from the bottom of the heel bone, and they are parallel to the ground. There is a nerve that runs very close to this area and may contribute to the pain which occurs.

The spur occurs where the plantar fascia attaches, and the pain in that area is really due to the plantar fascia attachment being irritated. However, there are many people with heel spurs who have no symptoms at all. Haglund's deformity is a bony growth on the back of the heel bone, which then irritates the bursa and the skin lying behind the heel bone. Achilles tendinopathy is degeneration of the tendon that connects your calf muscles to your heel bone. Stress fractures are common in military training.

Went to Podiatrist after receiving pain pills to move, got MRI and he told me I have severe tear in plantor faciitis tendon. Have swelling or what I call a fatty feeling, as I have always had on ball of foot below left most two toes. And it seems to feel a little more fatty since I walked for the first time today after putting on a good pair of ankle boots. Any idea what the fatty feeling is on ball of foot. Lastly, I took the boot off at my stairs into my house 2 days ago and took a step using ball of left foot and it did not pop.